Навигация
С инфинитивом без частицы to после глаголов
2. С инфинитивом без частицы to после глаголов
to let: Don't let them play in the street.
to make: Don't make me laugh.
3. С инфинитивом с частицей to после глаголов
to want I want you to find me a place in the first row.
to expect I expect you to come in time.
to believe I believe her to be a very good teacher.
to know I know him to be a good student.
to advise I advise you to enter the institute.
to consider The climate in England is considered to be mild.
to order He is ordered not to be late.
to allow They allow to use dictionaries at the exam.
to like I would like you to finish your work,
to find I find your story to be very interesting.
Exercise 8.2. Put the verbs in brackets in the right form:
1. He made me (do) it all over again. 2. Her father made her (learn) the lessons. 3. If you want us (make) the work quickly you should let us (start) at once. 4. Would you like me (read) now? 5. They won't let us (leave) the classroom till our control work has been checked. 6. He wouldn't let the children (play) in his study. 7. Please let me (know) the results of your exam as soon as possible. 8. He made us (wait) for two hours. 9. I let him (go) early as he had done his task. 10. I'd like him (enter) the university but I can't make him (do) it. 11. I want her (learn) English. 12. I heard the door (open) and saw my friend (come) into the room. 13. I heard her (play) the piano. 14. I saw him (go out) of the house. 15. The teacher advised us (use) dictionaries. 16. Her father doesn't allow her (go) to the cinema alone. 17. We expect our basketball team (win) next game. 18. We don't want you (tell) anything. 19. I saw them (open) the window. 20. That is too difficult for you to do, let me (help) you.
Exercise 8.3. Translate into English:
1. Вы хотите, чтобы дети играли здесь? 2. Вы хотите, чтобы мы встретились сегодня? 3. Вы ожидаете, работа будет сделана скоро? 4. Мы ожидаем, что они хорошо проведут у нас время. 5. Я хочу, чтобы он закончил эту работу. 6. Мы слышали, что она знает, когда мы сдаем экзамен. 7. Вы хотите, чтобы мы обсудили этот вопрос сегодня? 8. Мы ожидаем, что на этом месте будет построен новый дом. 9. Вы хотели бы, чтобы работа была сделана сегодня?
§2. Причастие и герундий. Их отличие
(Participle I)
Причастие I (причастие настоящего времени), образованное при помощи окончания -ing, имеет активную и страдательную формы:
активная (несовершенный вид) — asking,
активная (совершенный вид) — having asked.
страдательная (несовершенный) — being asked,
страдательная (совершенный) — having been asked.
Причастие I употребляется в функции:
1. Определения:
The man sitting at the table is our teacher. — Человек, сидящий за столом — наш учитель.
The houses being built in our town are not very high. — Дома, строящиеся в нашем городе, невысоки.
2. Обстоятельства:
Going home I met an old friend. — Идя домой, я встретил старого друга.
Having finished work I went home. — Закончив работу, я пошел домой.
Причастие II (Participle II)
Причастие II (причастие прошедшего времени) всегда пассивно. Образуется оно прибавлением суффикса -ed к основе правильного глагола или путем чередования звуков в корне неправильного глагола.
Причастие II употребляется в функции:
1. Определения.
The book translated from English is interesting. — Книга, переведенная с английского языка, интересная.
2. Обстоятельства (причины и времени):
Given the task he began to work. — Когда ему дали задание он начал работать.
Употребление герундия и его отличие от причастия I
Причастие — неличная форма глагола, промежуточная между глаголом и прилагательным:
The boy playing in the yard is my brother, — Мальчик, (какой?) играющий во дворе, — мой брат.
Герундий также является неличной формой глагола, промежуточной между существительным и глаголом:
Smoking is harmful. — Курение (что?) вредно.
Иными словами, причастие—в большей степени «прилагательное» по своим функциям, герундий — «существительное».
Герундий употребляется:
1. в качестве подлежащего:
Reading is useful.
2. как часть сказуемого после глаголов to finish, to start, to continue, to go on, to keep и др.
He started reading the book.
3. как предложное дополнение: I am fond of reading.
4. как прямое дополнение: Do you mind my reading here?
5. как обстоятельство времени: After reading he closed the book.
6. как обстоятельство образа действия: Instead of reading he went to the movies.
Активная форма герундия: giving, beating.
Пассивная форма герундия: being given, being beaten.
Exercise 8.4. Open the brackets using the gerund:
1. The grass in the garden is very dry, it needs (water). 2. It's very warm outside. You don't need (put on) yourcoat. 3. The house is old, and it wants (repair). 4. Famous people don't need (introduce) themselves. 5. The carpet is covered with dust, it needs (sweep). 6. The shoes are very dirty, they need (polish). 7. These shoes have a hole, they want (mend). 8. The table cloth is quite clean, it doesn't want (wash) yet. 9. The room needed (clean). 10. (learn) foreign languages is very useful. 12. I know my hair wants (cut) but I never have time to go to the hairdresser's. 13. John needed (cheer up) when he heard that he'd failed his exams. 14. You should tidy up the garden. — Yes, it needs (tidy). The roses want (water), the peaches want (pick), the grass wants (cut).
UNIT 9 MY FUTURE PROFESSION
I. Звуки [au], [dr], [br], [gr], [tr], [fr], [qr].
II. Text A: «My future profession»,
Text B: «The Future of the engineering profession»
III.§1. Придаточные предложения условия и времени, действие которых отнесено к будущему.
§2. Сослагательное наклонение в условных предложениях.
| Exercise A now — how — brown out — now — house louse — mouse — cows out — loud — without Exercise В | brain — brakes — brand brunch — branch — brave Brazil — breach — break breath — broth — breathe Exercise D treasure — trainer — trench |
| draw — dribble — draft drag — drab — drank drain — dragon — drama drape — dreadful — drugs Dresden — dress — dry drill — drop — drink drive — drown — drum drift — drier — droopy Exercise С brown — bread — brace | track — trade — traffic troops — trend — trail translate — transmit — trance Exercise E France — French — fruit fry — frame — free three — thread — throat threat — through — thrill thirty — throne — threaten |
Hi, there! Here is Ann Sokolova again. I am afraid this will be my last meeting with you because I need to pack my suitcase. I am leaving for Sochi tonight. I have passed all the exams successfully and I'm free till the 1st of September.
As I have already told you, I was always good in mathematics and physics. My parents bought me a computer when I was in the 10th form. Since then I knew that I would become a specialist in computer technologies — a computer engineer.
Computer industry is developing so fast, that it comprises almost all spheres of professional life. No business now is possible without computers. This is especially true about automated manufacturing of products and robotics. Computer control of automated production opens new horizons for the cheap and quality production of goods. Information is now generated, transmitted, received, and stored electronically through computer networks on a scale unprecedented in history, and there is every indication that the explosive rate of growth in this field will continue.
Computer engineering is a general field. It deals with both electric and electronic industries.
Electronic engineering deals with the research, design, integration, and application of circuits and devices used in the transmission and processing of information.
Engineers in the field of electric and electronic engineering are concerned with all aspects of electrical communications, from fundamental questions such as «What is information?» to the highly practical, such as the design of telephone systems. In designing communication systems, engineers rely on various branches of advanced mathematics, such as Fourier analysis, linear systems theory, linear algebra, differential equations, and probability theory.
Engineers work on control systems which are used extensively in automated manufacturing and in robotics.
Major developments in the field of communications and control have been the replacement of analogue systems with digital systems; fibre optics are used now instead of copper cables. Digital systems offer far greater immunity to electrical noise. Fibre optics are likewise immune to interference; they also have great carrying capacity, and are extremely light and inexpensive to manufacture.
Computer engineering is now the most rapidly growing field. The electronics of computers is the design and manufacture of memory systems, of central processing units, and of peripheral devices. The most prospective industry now is the Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) and new computer architectures. The field of computer science is closely related to computer engineering; however, the task of making computers more «intelligent» (artificial intelligence), through creation of sophisticated programs or development of higher level machine languages or other means, is generally regarded as the dream of computer science.
One current trend in computer engineering is microminiaturization. Engineers continue to work to fit greater and greater numbers of circuit elements onto smaller and smaller chips.
Another trend is towards increasing the speed of computer operations through the use of parallel processors and superconducting materials.
So, as you see, there are a lot of employment opportunities in my field. I don't worry about finding a job. The most important thing for me now is to study well and to graduate from the Academy.
Vocabulary:
to comprise — включать в себя
automated manufacturing of products — автоматизированное производство товаров
robotics — робототехника
horizons — горизонты
cheap — дешевый
to generate — генерировать, производить
to transmit — передавать
to store — хранить
scale — масштаб
unprecedented in history — не имеющий прецедентов в истории
indication — указание, свидетельство
explosive — взрывной
to deal with — иметь дело с, заниматься чем-либо
integration — интеграция
application — приложение, использование
circuits — электрические схемы, цепи
device — устройство
transmission — передача
processing — обработка
to rely — полагаться
Fourier analysis — анализ Фурье
linear systems theory — теория линейных систем
linear algebra — линейная алгебра
differential equations — дифференциальные уравнения
probability theory — теория вероятности
extensively — широко
replacement — замещение
fibre optics — оптоволоконные технологии
copper — медь
digital — цифровой
immunity — защищенность, невосприимчивость
carrying capacity — пропускная способность
light — легкий
rapidly growing — быстрорастущий
artificial intelligence — искусственный разум
sophisticated — сложный
superconducting — сверхпроводимость
ADD TO YOUR ACTIVE VOCABULARY:
a) mechanical engineer — инженер-механик
electric engineer — инженер-электрик
electronic engineer — инженер электроник
computer engineer — инженер-компьютерщик
military engineer — военный инженер
b) prestigious job (work) — престижная работа
well-paid job — высокооплачиваемая работа
employee — наемный рабочий
employer — наймодатель
businessman — предприниматель, бизнесмен
state-employed — государственный служащий
white-collar worker — «белый воротничок», работник умственного труда
blue-collar worker — «синий воротничок», работник физического труда
skilled worker — квалифицированный рабочий
unskilled worker — неквалифицированный рабочий
experienced worker — опытный работник
c) to be hired for a job — быть нанятым на выполнение работы
to look for a new job (work, position) — искать новую работу
to apply for a new job — претендовать на какую-либо должность
application for a position of — заявление на какую-либо должность
resume — резюме
C.V. (curriculum vitae) — автобиография
to be fired — быть уволенным
to retire — уходить на пенсию
to be unemployed — быть безработным
Exercise 9.1. Translate into English:
1. Родители купили мне компьютер, когда я училась(ся) в десятом классе.
2. Никакой современный бизнес не возможен без компьютерной техники.
3. Компьютерная индустрия — наиболее быстроразвивающеся производство.
4. Компьютерное управление автоматизированными производственными линиями открывает новые горизонты дешевого и качественного производства товаров.
5. Крупным достижением в сфере коммуникации является замена аналоговых систем на цифорвые.
6. В настоящее время оптоволоконные цифровые технологии обеспечивают более качественную и доступную связь, чем аналоговые системы.
Exercise 9.2. How do you see your future profession? Please answer the following questions:
1) What kind of work are you interested in?
a) well paid
b) interesting
c) in a large and famous company
d) quiet
e) in an industry which has a future
f) prestigious
g) not to sit the whole day in the office
h) to travel a lot
2) What position would you like to have?
a) to manage people — manager
b) to work for someone else — an employee
c) to be your own boss — self-employed, businessman
d) to be responsible for everything — top manager, director
e) to work for the state — state employee
Exercise 9.3. Please discuss with your group advantages and disadvantages of your future profession. Do you think that engineering profession is prestigios? Is it well-paid? How difficult is it to find a good work in this field?
Text B «THE FUTURE OF THE ENGINEERING PROFESSION»
Among various recent trends in the engineering profession computerization is the most widespread. The trend in modern engineering offices is also towards computerization. Computers are increasingly used for solving complex problems as well as for handling, storing, and generating the enormous volume of data modern engineers must work with.
Scientific methods of engineering are applied in several fields not connected directly to manufacture and construction. Modern engineering is characterized by the broad application of what is known as systems engineering principles.
Engineers in industry work not only with machines but also with people, to determine, for example, how machines can be operated most efficiently by workers. A small change in the location of the controls of a machine or of its position with relation to other machines or equipment, or a change in the muscular movements of the operator, often results in greatly increased production. This type of engineering work is called time-study engineering.
A related field of engineering, human-factors engineering, also known as ergonomics, received wide attention in the late 1970s and 1980s when the safety of nuclear reactors was questioned following serious accidents that were caused by operator errors, design failures, and malfunctioning equipment.
Human-factors engineering seeks to establish criteria for the efficient, human-centred design of, among other things, the large, complicated control panels that monitor and govern nuclear reactor operations.
General understanding:
1. What is the most widespread trend in the engineering profession?
2. What are computers used for in modern engineering?
3. What approaches are used in modern engineering?
4. What is «ergonomics»?
5. What does human-factors engineering deal with?
GRAMMAR
§1. Придаточные предложения условия и времени, действие которых отнесено к будущему
В придаточных предложениях условия и времени с союзами
If (если),
when (когда),
after (после),
before (перед тем, как),
as soon as (как только), ]
unless (если не),
until (до тех пор, пока не),
будущее время заменяется формой настоящего времени, но на русский язык переводится будущим, например:
If you help me, I shall do this work. — Если ты поможешь мне, я сделаю эту работу.
As soon as I get free, I'll come to you. — Как только я освобожусь, я приду к тебе.
We shall not begin until you come. — Мы не начнем, пока ты не придешь.
Exercise 9.4. Open the brackets and put the verbs in the right form:
1. He (go) out when the weather (get) warmer. 2. I (wait) for you until you (come) back from school. 3. I'm afraid the train (start) before we (come) to the station. 4. We (go) to the country tomorrow if the weather (to be) fine. 5. We (not pass) the examination next year if we not (work) harder. 6. If you (not drive) more carefully you (have) an accident. 7. You (be) late if you (not take) a taxi. 8. I (finish) reading this book before I (go) to bed. 9. You must (send) us a telegram as soon as you (arrive). 10. We (have) a picnic tomorrow if it (be) a fine day. 11. We (go) out when it (stop) raining. 12. We (not to have) dinner until you (come). 13. I'm sure they (write) to us when they (know) our new address.
Прочитайте примеры и запомните наиболее употребительные суффиксы существительных
-ег/ог — teacher, writer, actor, doctor
-ist — scientist, artist, dentist
-ment — government, movement, development
-(t)ion — revolution, translation, operation
-ity/ty — popularity, honesty, ability
-sion/ssion — revision, session, discussion,
-ness — happiness, illness, darkness
Прочитайте примеры и запомните наиболее употребительные суффиксы и префиксы глаголов.
re- — rewrite, rebuild, reconstruct,
mis- — misprint, misunderstand, miscount.
Прочитайте примеры и запомните наиболее употребительные суффиксы и префиксы прилагательных.
un- — unhappy, unable, uncomfortable
dis- — dishonest, discouraging, disconnectng
Прочитайте примеры и запомните основные суффиксы числительных.
-teen — fifteen, sixteen, eighteen
-ty — twenty, thirty, sixty, ninety
-th — fourth, seventh, eighteenth
Exercise 9.5. Make up adjectives from the following words:
colour, beauty, peace, use, hope, truth, rain, help, power, pain, care.
§2. Сослагательное наклонение в условных предложениях
Сослагательное наклонение выражает возможность, нереальность, предположительность действия.
Изъявительное наклонение.
If I learn his address I shall write to him. — Если я узнаю его адрес, я ему напишу.
Сослагательное наклонение:
If I knew his address I would write to him. — Если бы я знал его адрес (сейчас), я написал бы ему (сейчас или в ближайшем будущем). Глагол в придаточном предложении — в форме Past Indefinite, в главном — в форме Future in the Past.
В случае, если действие, описываемое сослагательным наклонением, относится к прошедшему времени, в главном предложении используется форма будущего совершенного с точки зрения прошедшего Future Perfect in the Past, а в придаточном — прошедшее совершенное Past Perfect.
If I had known his address I would have written to him. — Если бы я знал его адрес (в прошлом), я написал бы ему (в прошлом же).
I wish I lived not far from here. (настоящее время). —Жаль, что я не живу поблизости.
I wish I had lived not far from here (прошедшее время). — Жаль, что я не жил поблизости.
Exercise 9.6. Translate into Russian:
1. If I came later I would be late for the lesson. 2. If he had known the time-table he wouldn't have missed the train. 3. It would be better if you learned the oral topics. 3. I wish I had known this before the examination. 4. I would have come to you if you had not lived so far away. 5. If I had seen you yesterday I would have given you my text-book. 6. If I were in your place I wouldn't buy the tickets beforehand. 7. If I had known that you needed help I would have helped you.
UNIT 1
METALS
I. Text A: «Metals», Text B: «Steel», Text C: «Methods of steel heat treatment»
II. Famous Scientists. Dmitry Ivanovlch Mendeleyev.
Text A: «METALS»
Metals are materials most widely used in industry because of their properties. The study of the production and properties of metals is known as metallurgy.
The separation between the atoms in metals is small, so most metals are dense. The atoms are arranged regularly and can slide over each other. That is why metals are malleable (can be deformed and bent without fracture) and ductile (can be drawn into wire). Metals vary greatly in their properties. For example, lead is soft and can be bent by hand, while iron can only be worked by hammering at red heat.
The regular arrangement of atoms in metals gives them a crystalline structure. Irregular crystals are called grains. The properties of the metals depend on the size, shape, orientation, and composition of these grains. In general, a metal with small grains will be harder and stronger than one with coarse grains.
Heat treatment such as quenching, tempering, or annealing controls the nature of the grains and their size in the metal. Small amounts of other metals (less than 1 per cent) are often added to a pure metal. This is called alloying (легирование) and it changes the grain structure and properties of metals.
All metals can be formed by drawing, rolling, hammering and extrusion, but some require hot-working. Metals are subject to metal fatigue and to creep (the slow increase in length under stress) causing deformation and failure. Both effects are taken into account by engineers when designing, for example, airplanes, gas-turbines, and pressure vessels for high-temperature chemical processes. Metals can be worked using machine-tools such as lathe, milling machine, shaper and grinder.
The ways of working a metal depend on its properties. Many metals can be melted and cast in moulds, but special conditions are required for metals that react with air.
Vocabulary:
property — свойство
metallurgy — металлургия
separation — разделение, отстояние
dense — плотный
arrangement — расположение
regularly — регулярно, правильно
to slide — скользить
malleable — ковкий, податливый, способный деформироваться
bent pp of bend — гнуть
to fracture — ломать
ductile — эластичный, ковкий
to draw — волочить, тянуть
wire — проволока
lead — свинец
iron — железо, чугун
grain — зерно
to depend — зависеть
size — размер, величина
shape — форма, формировать
composition — состав
coarse — грубый, крупный
treatment — обработка
quenching — закалка
tempering — отпуск после закалки, нормализация
annealing — отжиг, отпуск
rolling — прокатка
to hammer — ковать (напр. молотом)
extrusion — экструзия
metal fatigue — усталость металла
creep — ползучесть
stress — давление,
failure — повреждение, разрушение
vessel — сосуд, котел, судно
lathe — токарный станок
milling machine — фрезерный станок
shaper — строгальный станок
grinder — шлифовальный станок
to melt — плавить, плавиться расплавить
to cast — отливать, отлить
mould — форма (для отливки)
General understanding:
1. What are metals and what do we call metallurgy?
2. Why are most metals dense?
3. Why are metals malleable?
4. What is malleability?
5. What are grains?
6. What is alloying?
7. What is crystalline structure?
8. What do the properties of metals depend on?
9. What changes the size of grains in metals?
10. What are the main processes of metal forming?
11. How are metals worked?
12. What is creeping?
Exercise 1.1. Find the following words and word combinations in the text:
1. Свойства металлов
2. расстояние между атомами
3. правильное расположение
4. сильно отличаются по своим свойствам
5. кристаллическая структура
6. размер зерен
7. форма зерен
8. закалка
9. отжиг
10.волочение
11.прокатка
12.ковка
13.экструзия
14. структура и свойства зерна
15. горячая обработка
16. усталость металла
17. ползучесть металла
18. плавка и отливка в формы
19. способы обработки металлов
Exercise 1.2. Complete the following sentences:
1. Metals are...
2. Metallurgy is...
3. Most metals are...
4. The regular arrangement of atoms in metals...
5. Irregular crystals...
6. The properties of the metals depend...
7. Metals with small grains will be...
8....controls the nature of the grains in the metal.
9. Alloying is...
10. All metals can be formed by...
11. Creep is...
12. Metals can be worked using...
Exercise 1.3. Explain in English the meaning of the following words:
1. malleability
2. crystalline structure
3. grains
4. heat treatment
5. alloying
6. creep
Exercise 1.4. Translate into English:
1. Металлы — плотные материалы потому, что между атомами в металлах малое расстояние.
2. Металлы имеют кристаллическую структуру из-за правильного расположения атомов.
3. Чем меньше зерна, тем тверже металл.
4. Закалка и отжиг изменяют форму и размер зерен в металлах.
5. Легирование изменяет структуру зерен и свойства металлов.
6. Металл деформируется и разрушается из-за усталости и ползучести.
Text В: «STEEL»The most important metal in industry is iron and its alloy — steel. Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It is strong and stiff, but corrodes easily through rusting, although stainless and other special steels resist corrosion. The amount of carbon in a steel influences its properties considerably. Steels of low carbon content (mild steels) are quite ductile and are used in the manufacture of sheet iron, wire, and pipes. Medium-carbon steels containing from 0.2 to 0.4 per cent carbon are tougher and stronger and are used as structural steels. Both mild and medium-carbon steels are suitable for forging and welding. High-carbon steels contain from 0.4 to 1.5 per cent carbon, are hard and brittle and are used in cutting tools, surgical instruments, razor blades and springs. Tool steel, also called silver steel, contains about 1 per cent carbon and is strengthened and toughened by quenching and tempering.
The inclusion of other elements affects the properties of the steel. Manganese gives extra strength and toughness. Steel containing 4 per cent silicon is used for transformer cores or electromagnets because it has large grains acting like small magnets. The addition of chromium gives extra strength and corrosion resistance, so we can get rust-proof steels. Heating in the presence of carbon or nitrogen-rich materials is used to form a hard surface on steel (case-hardening). High-speed steels, which are extremely important in machine-tools, contain chromium and tungsten plus smaller amounts of vanadium, molybdenum and other metals.
Vocabulary:
alloy — сплав
carbon— углерод
stiff — жесткий
to corrode — разъедать, ржаветь
rusty — ржавый
stainless — нержавеющий
to resist — сопротивляться
considerably — значительно, гораздо
tough — крепкий, жесткий, прочный, выносливый
forging — ковка
welding — сварка
brittle — хрупкий, ломкий
cutting tools — режущие инструменты
surgical instruments — хирургические инструменты
blade — лезвие
spring — пружина
inclusion — включение
to affect — влиять
manganese — марганец
silicon — кремний
rust-proof — нержавеющий
nitrogen — азот
tungsten — вольфрам
General understanding:
1. What is steel?
2. What are the main properties of steel?
3. What are the drawbacks of steel?
4. What kinds of steel do you know? Where are they used?
5. What gives the addition of manganese, silicon and chromium to steel?
6. What can be made of mild steels (medium-carbon steels, high-carbon steels)?
7. What kind of steels can be forged and welded?
8. How can we get rust-proof (stainless) steel?
9. What is used to form a hard surface on steel?
10. What are high-speed steels alloyed with?
Exercise 1.5. Find the following words and word combinations in the text:
1. сплав железа и углерода
2. прочный и жесткий
3. легко коррозирует
4. нержавеющая сталь
5. низкое содержание углерода
6. ковкость
7. листовое железо, проволока, трубы
8. конструкционные стали
9. пригодны для ковки и сварки
10. твердый и хрупкий
11. режущие инструменты
12. хирургические инструменты
13. инструментальная сталь
14.упрочнять
15. добавление марганца (кремния, хрома, вольфрама, молибдена, ванадия)
Text С: «METHODS OF STEEL HEAT TREATMENT»
Quenching is a heat treatment when metal at a high temperature is rapidly cooled by immersion in water or oil. Quenching makes steel harder and more brittle, with small grains structure.
Tempering is a heat treatment applied to steel and certain alloys. Hardened steel after quenching from a high temperature is too hard and brittle for many applications and is also brittle. Tempering, that is re-heating to an intermediate temperature and cooling slowly, reduces this hardness and brittleness. Tempering temperatures depend on the composition of the steel but are frequently between 100 and 650 °C. Higher temperatures usually give a softer, tougher product. The color of the oxide film produced on the surface of the heated metal often serves as the indicator of its temperature.
Annealing is a heat treatment in which a material at high temperature is cooled slowly. After cooling the metal again becomes malleable and ductile (capable of being bent many times without cracking).
All these methods of steel heat treatment are used to obtain steels with certain mechanical properties for certain needs.
Vocabulary:
to immerse — погружать
to apply — применять
intermediate — промежуточный
oxide film — оксидная пленка
annealing — отжиг, отпуск
cracking — растрескивание
General understanding:
1. What can be done to obtain harder steel?
2. What makes steel more soft and tough?
3. What makes steel more malleable and ductile?
4. What can serve as the indicator of metal temperature while heating it?
5. What temperature range is used for tempering?
6. What are the methods of steel heat treatment used for?
Exercise 1.6. Translate into English the following words and word combinations:
1. температура нормализации
2. мелкозернистая структура
3. быстрое охлаждение
4. закаленная сталь
5. состав стали
6. окисная пленка
7. индикатор температуры
8. медленное охлаждение
FAMOUS PEOPLE OF SCIENCE
Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleyev
Dmitry Ivanovich Mendeleyev is a famous Russian chemist. He is best known for his development of the periodic table of the properties of the chemical elements. This table displays that elements' properties are changed periodically when they are arranged according to atomic weight.
Mendeleyev was born in 1834 in Tobolsk, Siberia. He studied chemistry at the University of St. Petersburg, and in 1859 he was sent to study at the University of Heidelberg. Mendeleyev returned to St. Petersburg and became Professor of Chemistry at the Technical Institute in 1863. He became Professor of General Chemistry at the University of St. Petersburg in 1866. Mendeleyev was a well-known teacher, and, because there was no good textbook in chemistry at that time, he wrote the two-volume «Principles of Chemistry» which became a classic textbook in chemistry.
In this book Mendeleyev tried to classify the elements according to their chemical properties. In 1869 he published his first version of his periodic table of elements. In 1871 he published an improved version of the periodic table, in which he left gaps for elements that were not known at that time. His table and theories were proved later when three predicted elements: gallium, germanium, and scandium were discovered.
Mendeleyev investigated the chemical theory of solution. He found that the best proportion of alcohol and water in vodka is 40%. He also investigated the thermal expansion of liquids and the nature of petroleum.
In 1893 he became director of the Bureau of Weights and Measures in St. Petersburg and held this position until his death in 1907.
UNIT 2
METALWORKING
I. Text A: Metalworking processes: Rolling. Extrusion,
Text B: Drawing. Forging. Sheet metal forming,
Text C: Metalworking and Metal Properties.
II. Famous scientists. Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov.
Text A: «METALWORKING PROCESSES»
Metals are important in industry because they can be easily deformed into useful shapes. A lot of metalworking processes have been developed for certain applications. They can be divided into five broad groups:
1. rolling,
2. extrusion,
3. drawing,
4. forging,
5. sheet-metal forming.
During the first four processes metal is subjected to large amounts of strain (deformation). But if deformation goes at a high temperature, the metal will recrystallize — that is, new strain-free grains will grow instead of deformed grains. For this reason metals are usually rolled, extruded, drawn, or forged above their recrystallization temperature. This is called hot working. Under these conditions there is no limit to the compressive plastic strain to which the metal can be subjected.
Other processes are performed below the recrystallization temperature. These are called cold working. Cold working hardens metal and makes the part stronger. However, there is a limit to the strain before a cold part cracks.
Rolling
Rolling is the most common metalworking process. More than 90 percent of the aluminum, steel and copper produced is rolled at least once in the course of production. The most common rolled product is sheet. Rolling can be done either hot or cold. If the rolling is finished cold, the surface will be smoother and the product stronger.
Extrusion
Extrusion is pushing the billet to flow through the orifice of a die. Products may have either a simple or a complex cross section. Aluminum window frames are the examples of complex extrusions.
Tubes or other hollow parts can also be extruded. The initial piece is a thick-walled tube, and the extruded part is shaped between a die on the outside of the tube and a mandrel held on the inside.
In impact extrusion (also called back-extrusion) (штамповка выдавливанием), the workpiece is placed in the bottom of a hole and a loosely fitting ram is pushed against it. The ram forces the metal to flow back around it, with the gap between the ram and the die determining the wall thickness. The example of this process is the manufacturing of aluminum beer cans.
Vocabulary:
useful — полезный
shape — форма, формировать
rolling — прокатка
extrusion — экструзия, выдавливание
drawing — волочение
forging — ковка
sheet — лист
to subject — подвергать
amount — количество
condition — состояние, условие
perform — выполнять, проводить
to harden — делаться твердым, упрочняться
at least — по крайней мере
common — общий
billet — заготовка, болванка
orifice — отверстие
die — штамп, пуансон, матрица, фильера, волочильная доска
cross section — поперечное сечение
window frame — рама окна
tube — труба
hollow — полый
initial — первоначальный, начальный
thick-walled — толстостенный
mandrel — оправка, сердечник
impact — удар
loosely — свободно, с зазором
fitting — зд. посадка
ram — пуансон, плунжер
force — сила
gap — промежуток, зазор
to determine — устанавливать, определять
General understanding:
1. Why are metals so important in industry?
2. What are the main metalworking processes?
3. Why are metals worked mostly hot?
4. What properties does cold working give to metals?
5. What is rolling? Where is it used?
6. What is extrusion? What shapes can be obtained after extrusion?
7. What are the types of extrusion?
Exercise 2.1. Find the following in the text:
1. могут легко деформироваться
2. нужные формы
3. подвергать большим деформациям
4. зерна свободные от деформации
5. температура перекристаллизации
6. пластическая деформация сжатия
7. самый обычный процесс обработки металла
8. самое обычное изделие проката
9. отверстие фильеры
10. первоначальный
11. сложное сечение
12. пустотелые детали
13. свободно входящий плунжер
14. зазор между плунжером (пуансоном) и штампом
15. толщина стенки
Exercise 2.2. Translate into English:
1. Способность металла перекристаллизовываться при высокой температуре используется при горячей
обработке.
2. Перекристаллизация — это рост новых, свободных от деформации зерен.
3. Во время горячей обработки металл может подвергаться очень большой пластической деформации сжатия.
4. Холодная обработка делает металл тверже и прочнее, но некоторые металлы имеют предел деформации.
5. Листовой прокат может производиться горячим или холодным.
6. Поверхность холоднокатаного листа более гладкая и он прочнее.
7. Поперечное сечение фильеры для экструзии может быть простым или сложным.
8. Алюминиевые и медные сплавы являются наилучшими для экструзии из-за их пластичности при деформации.
9. Алюминиевые банки, тюбики для зубной пасты являются примерами использования штамповки выдавливанием.
10. Толщина стенки алюминиевой банки определяется зазором между пунсоном и штампом.
Text В: «DRAWING»Drawing consists of pulling metal through a die. One type is wire drawing. The diameter reduction that can be achieved in one die is limited, but several dies in series can be used to get the desired reduction.
Sheet metal formingSheet metal forming (штамповка листового металла) is widely used when parts of certain shape and size are needed. It includes forging, bending and shearing. One characteristic of sheet metal forming is that the thickness of the sheet changes little in processing. The metal is stretched just beyond its yield point (2 to 4 percent strain) in order to retain the new shape. Bending can be done by pressing between two dies. Shearing is a cutting operation similar to that used for cloth.
Each of these processes may be used alone, but often all three are used on one part. For example, to make the roof of an automobile from a flat sheet, the edges are gripped and the piece pulled in tension over a lower die. Next an upper die is pressed over the top, finishing the forming operation (штамповку), and finally the edges are sheared off to give the final dimensions.
ForgingForging is the shaping of a piece of metal by pushing with open or closed dies. It is usually done hot in order to reduce the required force and increase the metal's plasticity.
Open-die forging is usually done by hammering a part between two flat faces. It is used to make parts that are too big to be formed in a closed die or in cases where only a few parts are to be made. The earliest forging machines lifted a large hammer that was then dropped on the workpiece, but now air or steam hammers are used, since they allow greater control over the force and the rate of forming. The part is shaped by moving or turning it between blows.
Closed-die forging is the shaping of hot metal within the walls of two dies that come together to enclose the workpiece on all sides. The process starts with a rod or bar cut to the length needed to fill the die. Since large, complex shapes and large strains are involved, several dies may be used to go from the initial bar to the final shape. With closed dies, parts can be made to close tolerances so that little finish machining is required.
Two closed-die forging operations are given special names. They are upsetting and coining. Coining takes its name from the final stage of forming metal coins, where the desired imprint is formed on a metal disk that is pressed in a closed die. Coining involves small strains and is done cold. Upsetting involves a flow of the metal back upon itself. An example of this process is the pushing of a short length of a rod through a hole, clamping the rod, and then hitting the exposed length with a die to form the head of a nail or bolt.
Vocabulary:
to pull — тянуть
reduction — сокращение
to achieve — достигать
in series — серия, последовательно
beyond — выше, свыше
yield point — точка текучести металла
to retain — сохранять, удерживать
to bend — гнуть
shearing — обрезка, отрезание
edge — край
to grip — схватывать
lower die — нижний штамп
upper die — верхний штамп
forming operation — операция штампования
dimension — измерение, размеры
required — необходимый
increase — увеличение
open-die forging — ковка в открытом штампе (подкладном)
hammering — ковка, колотить
within — внутри, в пределах
to enclose — заключать
rod — прут, стержень
bar — прут, брусок
involved — включенный
tolerance — допуск
upsetting — высадка, выдавливание
blow — удар
coining — чеканка
imprint — отпечаток
clamp — зажим
to hit — ударять
General understanding:
1. How can the reduction of diameter in wire drawing be achieved?
2. What is sheet metal forming and where it can be used?
3. What is close-die forging?
4. What is forging?
5. What are the types of forging?
6. What types of hammers are used now?
7. Where are coining and upsetting used?
8. What process is used in wire production?
9. Describe the process of making the roof of a car.
Exercise 2.3. Find the following word combinations in the text:
1. протягивание металла через фильеру
2. волочение проволоки
3. уменьшение диаметра
4. толщина листа
5. растягивать выше точки текучести
6. сохранить новую форму
7. края отрезаются
8. конечные размеры
9. уменьшить необходимое усилие
10. увеличить пластичность металла
11. воздушные или паровые молоты
12. сила и скорость штампования
13. внутри стенок двух штампов
14. отделочная обработка
15. малые допуски
Exercise 2.4. Translate into English:
1. При волочении проволоки диаметр отверстия волочильной доски каждый раз уменьшается.
2. Штамповка листового металла включает в себя ковку, изгиб и обрезку.
3. Небольшая деформация листа при растяжении помогает сохранить новую форму детали.
4. Изменение формы при штамповке производится путем сжатия между двумя штампами.
5. Края листа при штамповке отрезаются для получения конечных размеров.
6. При проковке деталь должна быть горячей для уменьшения необходимых усилий и увеличения пластичности металла.
7. После ковки в закрытых штампах детали не требуют большой механической обработки.
8. При чеканке деформация металла невелика и отпечаток формируется на поверхности металла.
9. Высадка используется для изготовления головок гвоздей и болтов.
Text C: «METALWORKING AND METAL PROPETIES»
An important feature of hot working is that it provides the improvement of mechanical properties of metals. Hot-working (hot-rolling or hot-forging) eliminates porosity, directionality, and segregation that are usually present in metals. Hot-worked products have better ductility and toughness than the unworked casting. During the forging of a bar, the grains of the metal become greatly elongated in the direction of flow. As a result, the toughness of the metal is greatly improved in this direction and weakened in directions transverse to the flow. Good forging makes the flow lines in the finished part oriented so as to lie in the direction of maximum stress when the part is placed in service.
The ability of a metal to resist thinning and fracture during cold-working operations plays an important role in alloy selection. In operations that involve stretching, the best alloys are those which grow stronger with strain (are strain hardening) — for example, the copper-zinc alloy, brass, used for cartridges and the aluminum-magnesium alloys in beverage cans, which exhibit greater strain hardening.
Fracture of the workpiece during forming can result from inner flaws in the metal. These flaws often consist of nonmetallic inclusions such as oxides or sulfides that are trapped in the metal during refining. Such inclusions can be avoided by proper manufacturing procedures.
The ability of different metals to undergo strain varies. The change of the shape after one forming operation is often limited by the tensile ductility of the metal. Metals such as copper and aluminum are more ductile in such operations than other metals.
Vocabulary
feature — черта, особенность
to provide — обеспечивать
improvement — улучшение
property — свойство
eliminate — ликвидировать, исключать
porosity — пористость
directional — направленный
to segregate — разделять
casting — отливка
elongated — удлиненный
to weaken — ослабевать, ослаблять
transverse — поперечный
flow — течение, поток
finished — отделанный
thinning — утончение
fracture — разрушение
strain hardening — деформационное упрочнение
brass — латунь
beverage — напиток
can — консервная банка
to exhibit — проявлять
inner — внутренний
flaws — недостатки, дефекты кристаллической решетки
inclusion — включение
trapped — зд. заключенный
refining — очищать, очистка
to avoid — избегать
to undergo — подвергаться
tensile ductility — пластичность при растяжении
General understanding:
1. What process improves the mechanical properties of metals?
2. What new properties have hot-worked products?
3. How does the forging of a bar affect the grains of the metal? What is the result of this?
4. How are the flow lines in the forged metal oriented and how does it affect the strength of the forged part?
5. What are the best strain-hardening alloys? Where can we use them?
6. What are the inner flaws in the metal?
7. Can a metal fracture because of the inner flaw?
8. What limits the change of the shape during forming operations?
Exercise 2.5. Find the following in the text:
1. важная особенность горячей обработки
2. улучшение механических свойств металла
3. необработанная отливка
4. направление максимального напряжения
5. способность сопротивляться утончению и разрушению
6. проявлять большее деформационное упрочнение
7. разрушение детали при штамповке
8. внутренние дефекты в металле
9. неметаллические включения
10. способность металлов подвергаться деформации
11. ограничивается пластичностью металла при растяжении
Exercise 2.6. Translate into English:
1. Горячая обработка металла улучшает его механические свойства и устраняет пористость и внутренние дефекты.
2. Удлинение зерен в направлении текучести при ковке значительно улучшает прочность металла в этом направлении и уменьшает его прочность в поперечном.
3. Хорошая проковка ориентирует линии текучести в направлении максимального напряжения.
4. Деформационное упрочнение металла при холодной обработке очень важно для получения металлов с улучшенными свойствами.
5. Внутренние дефекты металла — это неметаллические включения типа окислов или сульфидов.
6. Изменение формы при штамповании металлических деталей ограничивается пластичностью металла при растяжении.
FAMOUS SCIENTISTS
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov was a famous Russian writer, chemist, and astronomer who made a lot in literature and science.
Lomonosov was born on November 19, 1711, in Denisovka (now Lomonosov), near Archangelsk, and studied at the University of the Imperial Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg. After studying in Germany at the Universities of Marburg and Freiberg, Lomonosov returned to St. Petersburg in 1745 to teach chemistry and built a teaching and research laboratory there four years later.
Lomonosov is often called the founder of Russian science. He was an innovator in many fields. As a scientist he rejected the phlogiston theory of matter commonly accepted at the time and he anticipated the kinetic theory of gases. He regarded heat as a form of motion, suggested the wave theory of light, and stated the idea of conservation of matter. Lomonosov was the first person to record the freezing of mercury and to observe the atmosphere of Venus during a solar transit.
Interested in the development of Russian education, Lomonosov helped to found Moscow State University in 1755, and in the same year wrote a grammar that reformed the Russian literary language by combining Old Church Slavonic with modern language. In 1760 he published the first history of Russia. He also revived the art of Russian mosaic and built a mosaic and colored-glass factory. Most of his achievements, however, were unknown outside Russia.
UNIT3
MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGYI. Text A: «Materials science and technology»,
Text B: «Mechanical Properties of Materials».
II. Famous people of science and technology: Igor Sikorskly, Andrey Tupolev.
Text A: «MECHANICAL PROPERTIES Of MATERIALS»
Materials Science and Technology is the study of materials and how they can be fabricated to meet the needs of modern technology. Using the laboratory techniques and knowledge of physics, chemistry, and metallurgy, scientists are finding new ways of using metals, plastics and other materials.
Engineers must know how materials respond to external forces, such as tension, compression, torsion, bending, and shear. All materials respond to these forces by elastic deformation. That is, the materials return their original size and form when the external force disappears. The materials may also have permanent deformation or they may fracture. The results of external forces are creep and fatigue.
Compression is a pressure causing a decrease in volume. When a material is subjected to a bending, shearing, or torsion (twisting) force, both tensile and compressive forces are simultaneously at work. When a metal bar is bent, one side of it is stretched and subjected to a tensional force, and the other side is compressed.
Tension is a pulling force; for example, the force in a cable holding a weight. Under tension, a material usually stretches, returning to its original length if the force does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Under larger tensions, the material does not return completely to its original condition, and under greater forces the material ruptures.
Fatigue is the growth of cracks under stress. It occurs when a mechanical part is subjected to a repeated or cyclic stress, such as vibration. Even when the maximum stress never exceeds the elastic limit, failure of the material can occur even after a short time. No deformation is seen during fatigue, but small localized cracks develop and propagate through the material until the remaining cross-sectional area cannot support the maximum stress of the cyclic force. Knowledge of tensile stress, elastic limits, and the resistance of materials to creep and fatigue are of basic importance in engineering.
Creep is a slow, permanent deformation that results from a steady force acting on a material. Materials at high temperatures usually suffer from this deformation. The gradual loosening of bolts and the deformation of components of machines and engines are all the examples of creep. In many cases the slow deformation stops because deformation eliminates the force causing the creep. Creep extended over a long time finally leads to the rupture of the material.
Vocabulary
bar— брусок, прут
completely — полностью, совершенно
compression — сжатие
creep — ползучесть
cross-sectional area — площадь поперечного сечения
cyclic stress — циклическое напряжение
decrease — уменьшение
elastic deformation — упругая деформация
elastic limit — предел упругости
exceed — превышать
external forces — внешние силы
fatigue — усталость металла
fracture — перелом, излом
loosen — ослаблять, расшатывать
permanent deformation — постоянная деформация
remaining — оставшийся
shear — срез
simultaneously — одновременно
to stretch — растягивать
technique — методы
tension — напряженность
to propagate — распространяться
to bend — гнуть, согнуть
to extend — расширять, продолжаться
to meet the needs — отвечать требованиям
to occur — происходить
to respond — отвечать реагировать
to suffer — страдать
torsion — кручение
twisting — закручивание, изгиб
volume — объем, количество
rupture — разрыв
General understanding:
1. What are the external forces causing the elastic deformation of materials? Describe those forces that change the form and size of materials.
2. What are the results of external forces?
3. What kinds of deformation are the combinations of tension and compression?
4. What is the result of tension? What happens if the elastic limit of material is exceeded under tension?
5. What do we call fatigue? When does it occur? What are the results of fatigue?
6. What do we call creep? When does this type of permanent deformation take place? What are the results of creep?
Exercise 3.1. Find the following in the text:
1. отвечать требованиям современной технологии
2. используя лабораторные методы
3. новые способы использования металлов
4. сжатие, растяжение, изгиб, кручение, срез
5. возвращать первоначальный размер и форму
6. внешняя сила
7. постоянная деформация
8. уменьшение объема
9. растягивающие и сжимающие силы
10. превышать предел упругости материала
11. повторяющиеся циклические напряжения
12. разрушение материала
13. развитие и распространение мелких трещин
14. сопротивление материалов ползучести и усталости
Exercise 3.2. Translate into English the following sentences:
1. Упругая деформация — это реакция всех материалов на внешние силы, такие, как растяжение, сжатие, скручивание, изгиб и срез.
2. Усталость и ползучесть материалов являются результатом внешних сил.
3. Внешние силы вызывают постоянную деформацию и разрушение материала.
4. Растягивающие и сжимающие силы работают одновременно, когда мы изгибаем или скручиваем материал.
5. Растяжение материала выше предела его упругости дает постоянную деформацию или разрушение.
6. Когда деталь работает долгое время под циклическими напряжениями, в ней появляются небольшие растущие трещины из-за усталости металла.
7. Ползучесть — это медленное изменение размера детали под напряжением.
Text В: «Mechanical Properties of Materials»
Density (specific weight) is the amount of mass in a unit volume. It is measured in kilograms per cubic metre. The density of water is 1000 kg/ m3 but most materials have a higher density and sink in water. Aluminium alloys, with typical densities around 2800 kg/ m3 are considerably less dense than steels, which have typical densities around 7800 kg/ m3. Density is important in any application where the material must not be heavy.
Stiffness (rigidity) is a measure of the resistance to deformation such as stretching or bending. The Young modulus is a measure of the resistance to simple stretching or compression. It is the ratio of the applied force per unit area (stress) to the fractional elastic deformation (strain). Stiffness is important when a rigid structure is to be made.
Strength is the force per unit area (stress) that a material can support without failing. The units are the same as those of Stiffness, MN/m2, but in this case the deformation is irreversible. The yield strength is the stress at which a material first deforms plastically. For a metal the yield strength may be less than the fracture strength, which is the stress at which it breaks. Many materials have a higher strength in compression than in tension.
Ductility is the ability of a material to deform without breaking. One of the great advantages of metals is their ability to be formed into the shape that is needed, such as car body parts. Materials that are not ductile are brittle. Ductile materials can absorb energy by deformation but brittle materials cannot.
Toughness is the resistance of a material to breaking when there is a crack in it. For a material of given toughness, the stress at which it will fail is inversely proportional to the square root of the size of the largest defect present. Toughness is different from strength: the toughest steels, for example, are different from the ones with highest tensile strength. Brittle materials have low toughness: glass can be broken along a chosen line by first scratching it with a diamond. Composites can be designed to have considerably greater toughness than their constituent materials. The example of a very tough composite is fiberglass that is very flexible and strong.
Creep resistance is the resistance to a gradual permanent change of shape, and it becomes especially important at higher temperatures. A successful research has been made in materials for machine parts that operate at high temperatures and under high tensile forces without gradually extending, for example the parts of plane engines.
Vocabulary
ability — способность
amount — количество
absorb — поглощать
amount — количество
application — применение
brittle — хрупкий, ломкий
car body — кузов автомобиля
constituent — компонент
crack — трещина
creep resistance — устойчивость к ползучести
definition — определение
density — плотность
ductility — ковкость, эластичность
failure — повреждение
gradual — постепенный
permanent — постоянный
rigid — жесткий
to sink — тонуть
square root — квадратный корень
stiffness — жесткость
strain — нагрузка, напряжение, деформация
strength — прочность
stress — давление, напряжение
tensile strength — прочность на разрыв
toughness — прочность, стойкость
yield strength — прочность текучести
Young modulus — модуль Юнга
General understanding:
1. What is the density of a material?
2. What are the units of density? Where low density is needed?
3. What are the densities of water, aluminium and steel?
4. A measure of what properties is stiffness? When stiffness is important?
5. What is Young modulus?
6. What is strength?
7. What is yield strength? Why fracture strength is always greater than yield strength?
8. What is ductility? Give the examples of ductile materials. Give the examples of brittle materials.
8. What is toughness?
9. What properties of steel are necessary for the manufacturing of: a) springs, b) car body parts, c) bolts and nuts, d) cutting tools?
10. Where is aluminium mostly used because of its light weight?
Exercise 3.3. Find the following words and word combinations in the text:
1. количество массы в единице объема
2. килограмм на кубический метр
3. мера сопротивления деформации
4. отношение приложенной силы на единицу площади к частичной упругой деформации
5. жесткая конструкция
6. прочность на сжатие
7. способность материала деформироваться не разрушаясь
8. поглощать энергию путем деформации
9. обратно пропорционально квадрату размера дефекта
10. постепенное изменение формы
11. повышенные температуры
12. высокие растягивающие усилия
Exercise 3.4. Translate into English the following:
1. Плотность измеряется в килограммах на кубический метр.
2. Большинство материалов имеют более высокую плотность, чем вода и тонут в воде.
3. Плотность материала очень важна, особенно в авиации.
4. Модуль Юнга — отношение приложенной силы к упругой деформации данного материала.
5. Чем более металл жесткий, тем менее он деформируется под нагрузкой.
6. Когда металл растягивают, он сначала течет, то есть пластически деформируется.
7. Свинец, медь, алюминий и золото — самые ковкие металлы.
8. Сопротивление ползучести является очень важным свойством материалов, которые используются в авиационных моторах.
«FAMOUS PEOPLE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING»
Sikorsky Igor Ivanovich was a well-known aircraft engineer and manufacturer.
Sikorsky was born in 1889 in Kiev, in the Ukraine, and got his education at the naval college in St. Petersburg, and later in Kiev and Paris. He was the first to make experiments in helicopter design. In 1913 he designed, built, and flew the first successful aeroplane. Later he built military aircrafts for Russia and France.
In 1919 Sikorsky moved to the United States and later helped to organize an aircraft company that produced a series of multiengine flying boats for commercial service. Sikorsky became an American citizen in 1928. In the late 1930s he returned to developing helicopters and produced the first successful helicopter in the west. Helicopters designed by Sikorsky were used mostly by the US Army Air Forces during World War II. He died in 1972 at the age of 83.
Tupolev Andrey Nikolayevich, famous aircraft designer, was born in 1888. He graduated from the Moscow Higher Technical School, where he designed the first Russian wind tunnel. He helped to found the Central Aerohydrodynamics Institute in 1918 and later worked as the head of its design bureau. During his career he directed the design of more than 100 military and commercial aircraft, including the TU-2 and TU-4 bombers used in the World War II. In 1955 he designed the TU-104, the first passenger jet airliner. His TU-144 supersonic jet liner began its commercial passenger flights in 1977.
UNIT 4
MACHINE-TOOLS
I. Text A: «Machine-tools», Text B: «Lathe»,
Text C: «Milling, boring, drilling machines. Shapers and Planers», Text D: «Dies»II. Famous people of science and technology: George Stephenson, Robert Slephenson.
Text A: «MACHINE-TOOIS»
Machine-tools are used to shape metals and other materials. The material to be shaped is called the workpiece. Most machine-tools are now electrically driven. Machine-tools with electrical drive are faster and more accurate than hand tools: they were an important element in the development of mass-production processes, as they allowed individual parts to be made in large numbers so as to be interchangeable.
All machine-tools have facilities for holding both the workpiece and the tool, and for accurately controlling the movement of the cutting tool relative to the workpiece. Most machining operations generate large amounts of heat, and use cooling fluids (usually a mixture of water and oils) for cooling and lubrication.
Machine-tools usually work materials mechanically but other machining methods have been developed lately. They include chemical machining, spark erosion to machine very hard materials to any shape by means of a continuous high-voltage spark (discharge) between an electrode and a workpiece. Other machining methods include drilling using ultrasound, and cutting by means of a laser beam. Numerical control of machine-tools and flexible manufacturing systems have made it possible for complete systems of machine-tools to be used flexibly for the manufacture of a range of products.
Vocabulary:
machine-tools — станки
electrically driven — с электроприводом
shape — форма
workpiece — деталь
accurate — точный
development — развитие
to allow — позволять, разрешать
interchangeable — взаимозаменяемый
facility — приспособление
relative —относительный
amount — количество
fluid — жидкость
to lubricate — смазывать
spark erosion — электроискровая обработка
discharge — разряд
by means of — посредством
beam — луч
drilling — сверление
flexible — гибкий
range — ассортимент, диапазон
Text B: «LATHE»
Lathe is still the most important machine-tool. It produces parts of circular cross-section by turning the workpiece on its axis and cutting its surface with a sharp stationary tool. The tool may be moved sideways to produce a cylindrical part and moved towards the workpiece to control the depth of cut. Nowadays all lathes are power-driven by electric motors. That allows continuous rotation of the workpiece at a variety of speeds. The modern lathe is driven by means of a headstock supporting a hollow spindle on accurate bearings and carrying either a chuck or a faceplate, to which the workpiece is clamped. The movement of the tool, both along the lathe bed and at right angle to it, can be accurately controlled, so enabling a part to be machined to close tolerances. Modern lathes are often under numerical control.
Vocabulary:
lathe — токарный станок
circular cross-section — круглое поперечное сечение
surface — поверхность
stationary — неподвижный, стационарный
sideways — в сторону
variety — разнообразие, разновидность
depth — глубина
headstock — передняя бабка
spindle — шпиндель
chuck — зажим, патрон
faceplate — планшайба
lathe bed — станина станка
to enable — давать возможность
tolerance — допуск
General understanding:
1. What are machine-tools used for?
2. How are most machine-tools driven nowadays?
3. What facilities have all machine-tools?
4. How are the cutting tool and the workpiece cooled during machining?
5. What other machining methods have been developed lately?
6. What systems are used now for the manufacture of a range of products without the use of manual labor?
7. What parts can be made with lathes?
8. How can the cutting tool be moved on a lathe?
9. How is the workpiece clamped in a lathe?
10. Can we change the speeds of workpiece rotation in a lathe?
11. What is numerical control of machine tools used for?
Exercise 4.1. Find English equivalents in the text:
1. обрабатываемый материал
2. электропривод
3. более точный
4. отдельные детали
5. процесс массового производства
6. приспособления для держания резца и детали
7. операции по механической обработке детали
8. высоковольтный разряд
9. сверление ультразвуком
10. резание с помощью лазерного луча
11. гибкие производственные системы
12. детали круглого сечения
13. поворачивать деталь вокруг ее оси
14. двигать в сторону, двигать по направлению к детали
15. глубина резания
16. непрерывное вращение детали
17. движение резца вдоль станины
Exercise 4.2. Translate into English:
1. Токарный станок позволяет производить детали круглого сечения.
2. Деталь зажимается в патроне или на планшайбе токарного станка.
3. Резец может двигаться как вдоль станины, так и под прямым углом к ней.
4. Современные токарные станки часто имеют цифровое управление.
Text С: «MILLING MACHINE»
In a milling machine the cutter (фреза) is a circular device with a series of cutting edges on its circumference. The workpiece is held on a table that controls the feed against the cutter. The table has three possible movements: longitudinal, horizontal, and vertical; in some cases it can also rotate. Milling machines are the most versatile of all machine tools. Flat or contoured surfaces may be machined with excellent finish and accuracy. Angles, slots, gear teeth and cuts can be made by using various shapes of cutters.
Drilling and Boring MachinesTo drill a hole usually hole-making machine-tools are used. They can drill a hole according to some specification, they can enlarge it, or they can cut threads for a screw or to create an accurate size or a smooth finish of a hole.
Drilling machines (сверлильные станки) are different in size and function, from portable drills to radial drilling machines, multispindle units, automatic production machines, and deep-hole-drilling machines.
Boring (расточка) is a process that enlarges holes previously drilled, usually with a rotating single-point cutter held on a boring bar and fed against a stationary workpiece.
Shapers and PlanersThe shaper (поперечно-строгальный станок) is used mainly to produce different flat surfaces. The tool slides against the stationary workpiece and cuts on one stroke, returns to its starting position, and then cuts on the next stroke after a slight lateral displacement. In general, the shaper can make any surface having straight-line elements. It uses only one cutting-tool and is relatively slow, because the return stroke is idle. That is why the shaper is seldom found on a mass production line. It is, however, valuable for tool production and for workshops where flexibility is important and relative slowness is unimportant.
The planer (продольно-строгальный станок) is the largest of the reciprocating machine tools. It differs from the shaper, which moves a tool past a fixed workpiece because the planer moves the workpiece to expose a new section to the tool. Like the shaper, the planer is intended to produce vertical, horizontal, or diagonal cuts. It is also possible to mount several tools at one time in any or all tool holders of a planer to execute multiple simultaneous cuts.
GrindersGrinders (шлифовальные станки) remove metal by a rotating abrasive wheel. The wheel is composed of many small grains of abrasive, bonded together, with each grain acting as a miniature cutting tool. The process gives very smooth and accurate finishes. Only a small amount of material is removed at each pass of the wheel, so grinding machines require fine wheel regulation. The pressure of the wheel against the workpiece is usually very light, so that grinding can be carried out on fragile materials that cannot be machined by other conventional devices.
Vocabulary:
milling machine — фрезерный станок
series — серия, ряд
cutting edge — режущий край, острие
circumference — окружность
to feed — подавать
longitudinal— продольный
horizontal — горизонтальный
vertical — вертикальный
versatile — универсальный
flat — плоский
contoured — контурный
angle — угол
slot — прорезь, паз
gear teeth — зубья шестерни
drill — дрель, сверло, сверлить
hole — отверстие
to enlarge — увеличивать
thread — резьба
portable — портативный
unit — единица, целое, узел
previously — ранее
to slide — скользить
stroke — ход
lateral — боковой
displacement — смещение
straight — прямой
idle — на холостом ходу
workshop — цех, мастерская
to mount — крепить
holder — держатель
to execute — выполнять
simultaneous — одновременный
multiple — многочисленный
grinder — шлифовальный станок
wheel — круг, колесо
bonded — скрепленный
to remove — удалять
pass — проход
fine — точный
conventional — обычный
device — устройство, прибор
fragile — хрупкий
General understanding:
1. What is the shape of a cutter in a milling machine?
2. What moves in a milling machine, a table or a cutter?
3. What possible movements has the table of a milling machine?
4. What kind of surfaces and shapes may be machined by a milling machine?
5. What can we use a drilling machine for?
6. What kinds of drilling machines exist?
7. What is rotated while boring, a cutter or a work-piece?
8. Describe the work of a shaper (planer).
9. What must be done to execute multiple simultaneous cuts on a planer?
10. What is the working tool in a grinder?
11. Can we obtain a very smooth surface after grinding and why? 12. Can we grind fragile materials and why?
Exercise 4.3. Translate into English:
1. Токарный станок все еще остается самым важным станком.
2. Все современные токарные станки оборудованы электроприводами.
3. Движение инструмента контролируется с высокой точностью.
4. Электропривод позволяет обрабатывать заготовку на различных скоростях.
Text D: «DIES»
Dies are tools used for the shaping solid materials, especially those employed in the pressworking of cold metals.
In presswork, dies are used in pairs. The smaller die, or punch, fits inside the larger die, called the matrix or, simply, the die. The metal to be formed, usually a sheet, is placed over the matrix on the press. The punch is mounted on the press and moves down by hydraulic or mechanical force.
A number of different forms of dies are employed for different operations. The simplest are piercing dies (пробивной штамп), used for punching holes. Bending and folding dies are designed to make single or compound bends. A combination die is designed to perform more than one of the above operations in one stroke of the press. A progressive die permits successive forming operations with the same die.
In coining, metal is forced to flow into two matching dies, each of which bears a engraved design.
Wiredrawing Dies
In the manufacture of wire, a drawplate (волочильная доска) is usually employed. This tool is a metal plate containing a number of holes, successively less in diameter and known as wire dies. A piece of metal is pulled through the largest die to make a coarse wire. This wire is then drawn through the smaller hole, and then the next, until the wire is reduced to the desired measurement. Wiredrawing dies are made from extremely hard materials, such as tungsten carbide or diamonds.
Thread-Cutting Dies
For cutting threads on bolts or on the outside of pipes, a thread-cutting die (резьбонарезная плашка) is used. It is usually made of hardened steel in the form of a round plate with a hole in the centre. The hole has a thread. To cut an outside thread, the die is lubricated with oil and simply screwed onto an unthreaded bolt or piece of pipe, the same way a nut is screwed onto a bolt. The corresponding tool for cutting an inside thread, such as that inside a nut, is called a tap (метчик).
Vocabulary:
chip — стружка
sharp — острый
friction — трение
content — содержание
range — диапазон
inexpensive — недорогой
to permit — позволять, разрешать
common — обычный
tungsten — вольфрам
ingredient — ингредиент
diamond — алмаз
tips — наконечники
ceramic — керамический
truing — правка, наводка, заточка
die — матрица, штамп
matrix — матрица
to employ — применять
to pierce — протыкать, прокалывать
to punch — пробивать отверстие
matching — сочетающийся, парный
coarse — грубый
wire — проволока
to draw — тащить, волочить
thread — резьба
hardened — закаленный
to lubricate — смазывать
to screw — привинчивать
nut — гайка
outside — наружный, внешний
inside — внутри, внутренний
Exercise 4.4. Find English equivalents in the text:
1. удалять металлическую стружку
2. острый режущий край
3. содержание углерода
4. режущая способность
5. сталь для скоростного резания
6. правка шлифовальных кругов
7. гидравлическое или механическое давление
8. различные формы штампов
Exercise 4.5. Translate the following sentences into Russian:
1. Все резцы и фрезы должны иметь острую режущую кромку.
2. Во время резания режущий инструмент и деталь имеют высокую температуру и должны охлаждаться.
3. Углеродистые стали часто используются для изготовления резцов потому, что они недорогие.
4. Быстрорежущие стали содержат вольфрам, хром и ванадий.
5. Алмазы используются для резания абразивных материалов и чистовой обработки поверхности твердых материалов.
6. Для различных операций используют различные штампы.
7. Волочильные доски для проволоки делаются из очень твердых материалов.
8. Резьбонарезные плашки и метчики используются для нарезки резьбы снаружи и внутри.
FAMOUS PEOPLE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
George Stephenson
George Stephenson was a British inventor and engineer. He is famous for building the first practical railway locomotive.
Stephenson was born in 1781 in Wylam, near Newcastle upon Tyne, Northumberland. During his youth he worked as a fireman and later as an engineer in the coal mines of Newcastle. He invented one of the first miner's safety lamps independently of the British inventor Humphry Davy. Stephenson's early locomotives were used to carry loads in coal mines, and in 1823 he established a factory at Newcastle for their manufacture. In 1829 he designed a locomotive known as the Rocket, which could carry both loads and passengers at a greater speed than any locomotive constructed at that time. The success of the Rocket was the beginning of the construction of locomotives and the laying of railway lines.
Robert Stephenson, the son of George Stephenson was a British civil engineer. He is mostly well-known known for the construction of several notable bridges.
He was born in 1803 in Willington Quay, near Newcastle upon Tyne, and educated in Newcastle and at the University of Edinburgh. In 1829 he assisted his father in constructing a locomotive known as the Rocket, and four years later he was appointed construction engineer of the Birmingham and London Railway, completed in 1838. Stephenson built several famous bridges, including the Victoria Bridge in Northumberland, the Britannia Bridge in Wales, two bridges across the Nile in Damietta in Egypt and the Victoria Bridge in Montreal, Canada. Stephenson was a Member of Parliament from 1847 until his death in 1859.
UNIT 5 PLASTICS
I. Text A: «Plastics», Text B: «Types of plastics», Text C: «Composite Materials»
II. Famous People of Science: Alfred Bernhard Nobel.
Text A: «PLASTICS»Plastics are non-metallic, synthetic, carbon-based materials. They can be moulded, shaped, or extruded into flexible sheets, films, or fibres. Plastics are synthetic polymers. Polymers consist of long-chain molecules made of large numbers of identical small molecules (monomers). The chemical nature of a plastic is defined by the monomer (repeating unit) that makes up the chain of the polymer. Polyethene is a polyolefin; its monomer unit is ethene (formerly called ethylene). Other categories are acrylics (such as polymethylmethacrylate), styrenes (such as polystyrene), vinys (such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC)), polyesters, polyurethanes, polyamides (such as nylons), polyethers, acetals, phenolics, cellulosics, and amino resins. The molecules can be either natural — like cellulose, wax, and natural rubber — or synthetic — in polyethene and nylon. In co-polymers, more than one monomer is used.
The giant molecules of which polymers consist may be linear, branched, or cross-linked, depending on the plastic. Linear and branched molecules are thermoplastic (soften when heated), whereas cross-linked molecules are thermosetting (harden when heated).
Most plastics are synthesized from organic chemicals or from natural gas or coal. Plastics are light-weight compared to metals and are good electrical insulators. The best insulators now are epoxy resins and teflon. Teflon or polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE) was first made in 1938 and was produced commercially in 1950.
Plastics can be classified into several broad types.
1. Thermoplastics soften on heating, then harden again when cooled. Thermoplastic molecules are also coiled and because of this they are flexible and easily stretched.
Typical example of thermoplastics is polystyrene. Polystyrene resins are characterized by high resistance to chemical and mechanical stresses at low temperatures and by very low absorption of water. These properties make the polystyrenes especially suitable for radio-frequency insulation and for parts used at low temperatures in refrigerators and in airplanes. PET (polyethene terephthalate) is a transparent thermoplastic used for soft-drinks bottles. Thermoplastics are also viscoelastic, that is, they flow (creep) under stress. Examples are polythene, polystyrene and PVC.
2. Thermosetting plastics (thermosets) do not soften when heated, and with strong heating they decompose. In most thermosets final cross-linking, which fixes the molecules, takes place after the plastic has already been formed.
Thermosetting plastics have a higher density than thermoplastics. They are less flexible, more difficult to stretch, and are less subjected to creep. Examples of thermosetting plastics include urea-formaldehyde or polyurethane and epoxy resins, most polyesters, and phenolic polymers such as phenol-formaldehyde resin.
Похожие работы
... compound-shortened word formed from a word combination where one of the components was shortened, e.g. «busnapper» was formed from « bus kidnapper», «minijet» from «miniature jet». In the English language of the second half of the twentieth century there developed so called block compounds, that is compound words which have a uniting stress but a split spelling, such as «chat show», «pinguin ...
... of job. Because I suppose if than marriage he must provide his family. And the young coups must that they meant for understand each other. Customs and holidays in English – speaking countries. - Customs and holidays in the urban community are of great importance for everyone. - I think no matter who the man might be he must know customs and holidays his country. What holidays do you ...
... was the first writer in Europe to formulate communist principals as a bases of society. The Renaisense in England. The prideses of Shakespeare. The most brilliant period of English literature was in the second half of the 16’th and begining of 17’th centure.Sometimes it’s called “Elizabethen age” after quen Elizabeth 5. England had become a geat world ...
... like that: what kinds of animals eat grass?» The boy brightened up. «Animals!» he exclaimed, «I thought you said admirals.» Unit 9 Grammar: 1. Passive Voice. 2. Пассивные конструкции характерные для английского языка. 3. Формы инфинитива. I. Language Practice 1. Practise the fluent reading and correct intonation: — Helölo, Tom! — Helølo, Nick ö. Here you ø are at ...

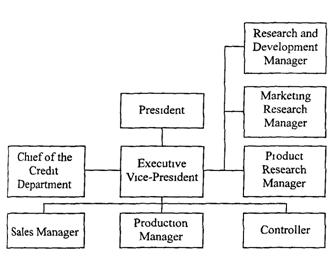
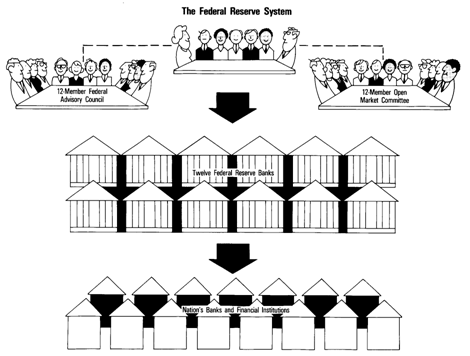

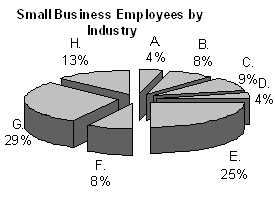
0 комментариев